Septic Systems
What is a septic tank: When you flush your toilet, take a shower, wash clothes, or do the dishes, wastewater enters a pipe that slopes toward your septic tank.
A septic tank is an underground container made of concrete. It treats the wastewater with the help of naturally occurring bacteria that break down solids and organic material.
When you start the process of designing a septic system, I will come to your location and take a soil sample. The sample will influence the type of system that you will need.
The wastewater leaving the tank is called effluent, it has been partially treated by the septic tank but still contains bacteria and pollutants so it receives further treatment before final dispersal.
Types of Septic Systems
An open discharge is a system that pumps effluent directly onto the ground surface. The effluent evaporates and absorbs into the soil. The wastewater first goes into a tank to be cleaned, before going into the pipe that leads to the ground.

To qualify: You need enough land to meet the proper amount of set backs:
- The distance from your discharge line to your property line must be a minimum of 300′
- Your discharge line to the house must be a minimum 150′
- Your discharge line to a water source (well, cistern, dug out etc.) must be a minimum of 165′
PROS
- Cheaper system
CONS
- It requires the right amount of set backs
- It requires a large amount of space (around 10-12 acres at least)
A holding tank is simply a tank that is in the ground, it needs to be pumped out by a vacuum truck.
To qualify: Most will qualify, as long as your county approves. Camrose county approves.
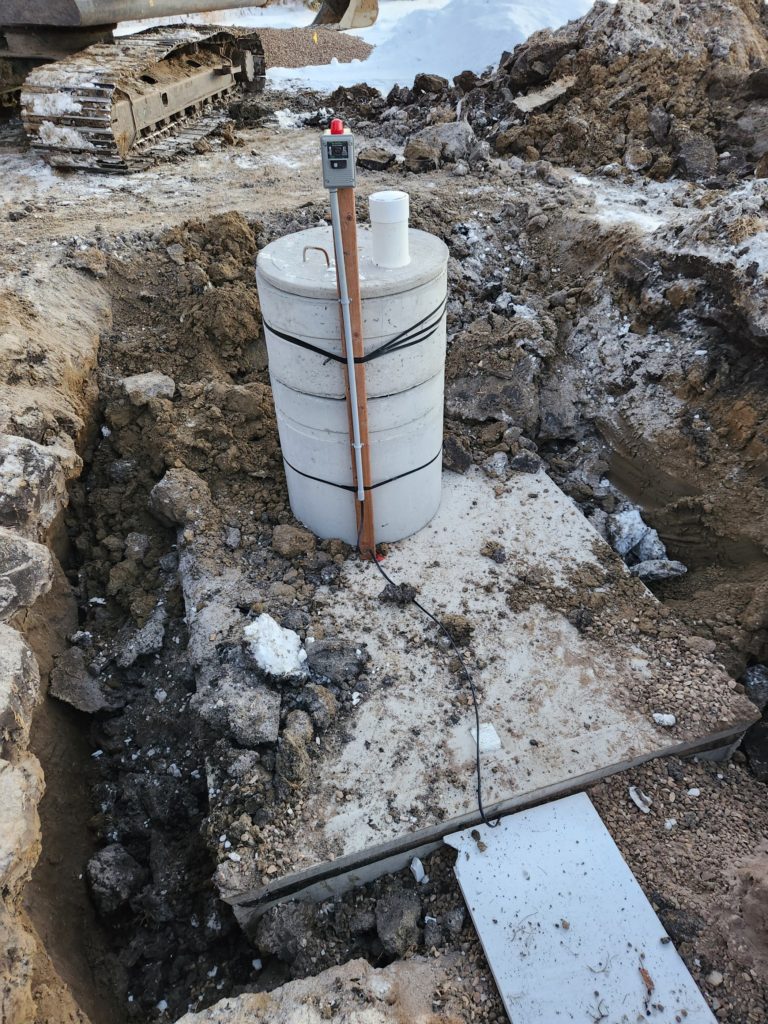

PROS
- Its fast to install
- The install is cheaper then other sysems
- The system doesn’t take up much space
CONS
- It requries an ongoing cost of hiring a VAC (vacume) truck to pump it out
- Having to keep an eye on it to see how full it is
A mound is a system that has a drain field that sits above ground in an engineered mound. It first goes into a tank to be cleaned, then goes through a pipe that leads to the mound system.
This system has pipes that disperse slowly and evenly through sand and gravel filled bed. The mound is covered with soil and will look like a hill on your property, it can be covered in vegetation, but not trees as the roots may disrupt the system. The vegetation will also help with additional filtration of the effluent.
To qualify: You need an area on your land that is flat virgin soil that is far enough from a waterway.
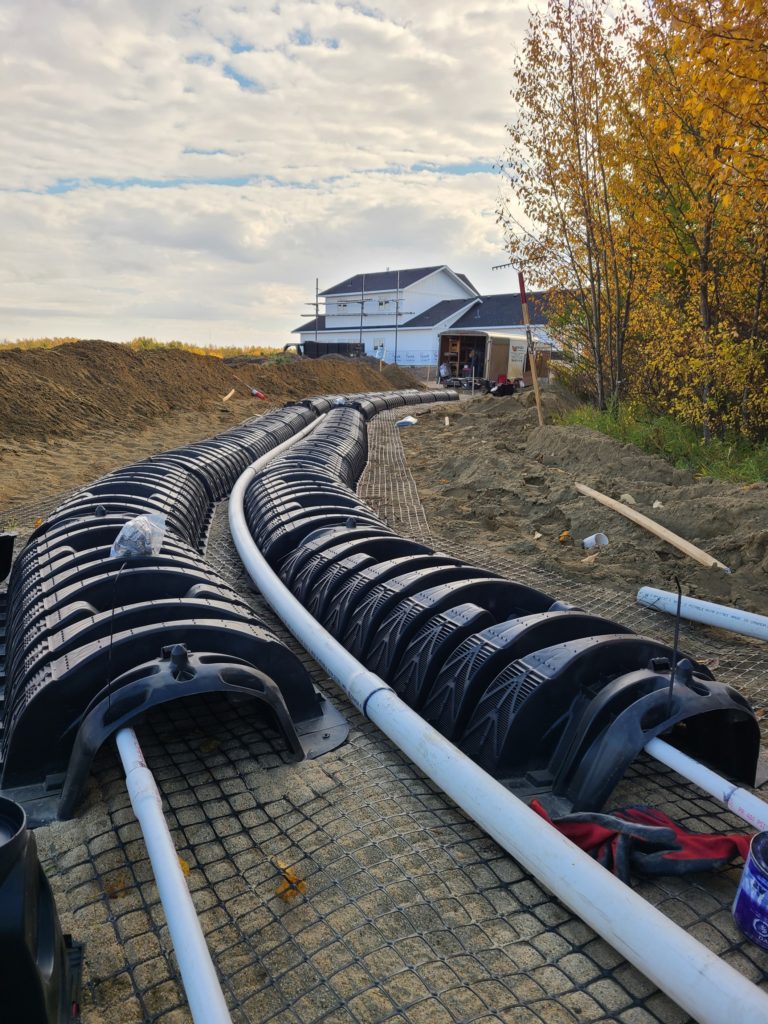

PROS
- Environment friendly, if you have a high water table it does a great job of keeping waste products away from the water table
- Your system is not as limited by low absorbing soil types
- It can work when you don’t have a large amount of space
- You can surround the mound in trees and trees will thrive since they will be well watered
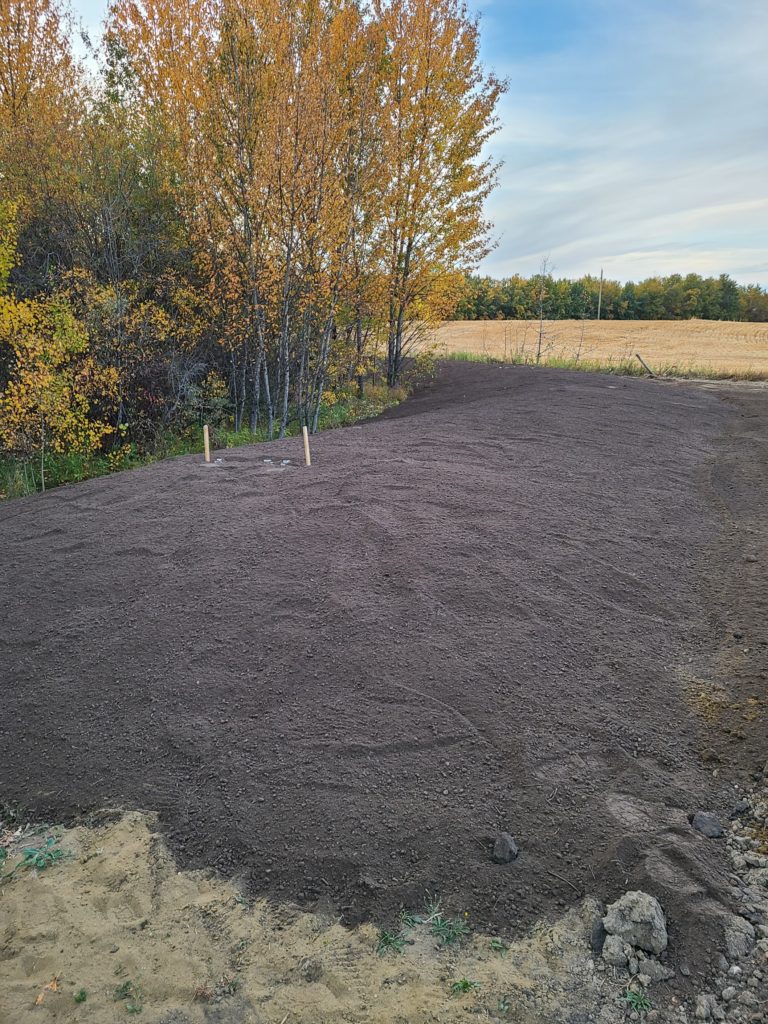

CONS
- You will have a mound of dirt on your property, you will need to landscape the dirt with grass to blend it into your landscape
- Can be expensive as it is a labor intensive system
An at-grade system accomplishes the final treatment by releasing the effluent into a forest floor. It first goes into a septic tank to clean, then it will need to go into a secondary treatment tank (which is an extra chamber) this creates an effluent that is clean enough to disperse into your forest floor.
To qualify: You must have a sizable forest, it must have a forest floor that consists of a thicker hummus layer (around 6-8″).
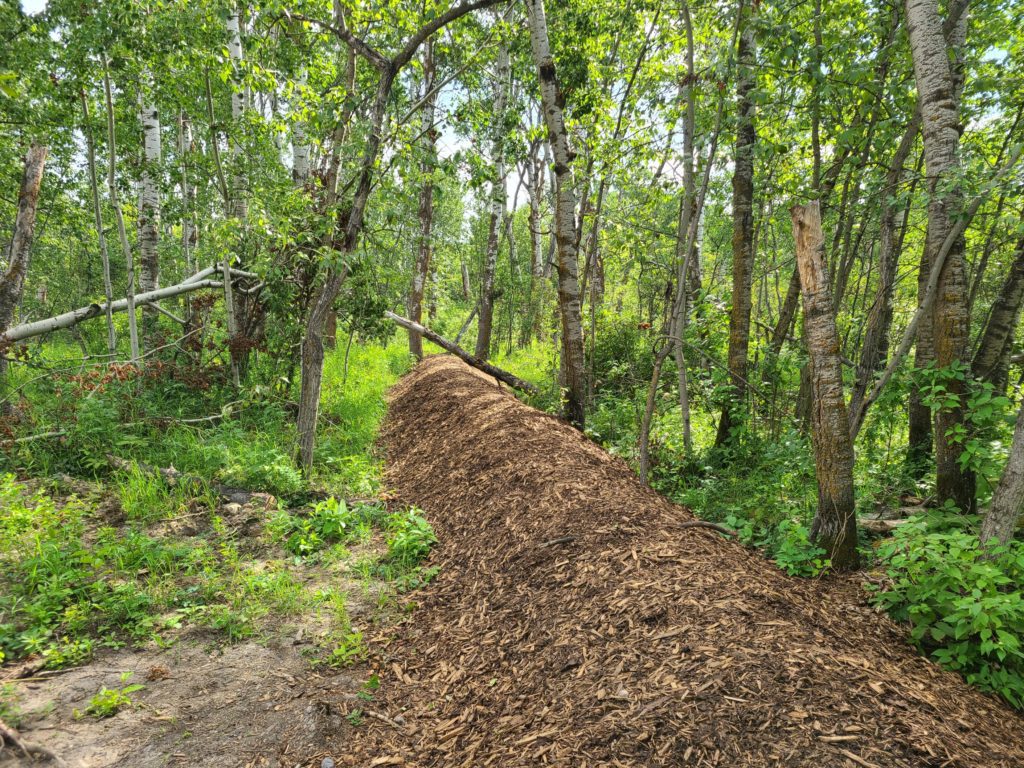

PROS
- Great if your land doesn’t have a large drainage field
- It is hidden in the trees
- It supports the vegetative growth by watering the trees
- It doesn’t take up much space
CONS
- It can require more maintenance since there are more movable parts
- It can be expensive
A field is when you dig trenches for a series of perforated pipes that disperse the effluent slowly into the soil.
PROS
- You don’t see it
- Easy to mow since the vegetation that grows over it will be flat
CONS
- It requires good soil depth (high absorption) of at least 8′
- It can be very labor intensive to build
- It takes up a lot of space underground that needs to be dedicated to it